Steps/algorithm:
1. Chose/decide a root bridge
2. Set the chosen root bridge bridge priority. Because switch priority is the only variable the used as spanning-tree root bridge calculation.
3. Set spanning-tree port fast to every ports that connect the client to switch. Do not set spanning-tree to port(s) that connect to switch to switch.
Topology or network diagram:
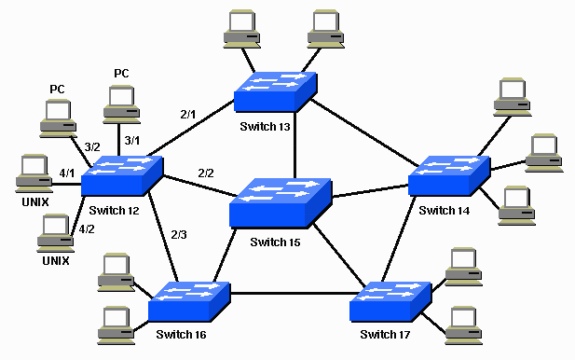
In above topology, switch 15 is suitable as backbone switch.
Source of reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/5234-5.html
Troubleshoot commands:
1. Chose/decide a root bridge
2. Set the chosen root bridge bridge priority. Because switch priority is the only variable the used as spanning-tree root bridge calculation.
3. Set spanning-tree port fast to every ports that connect the client to switch. Do not set spanning-tree to port(s) that connect to switch to switch.
Topology or network diagram:

In above topology, switch 15 is suitable as backbone switch.
Source of reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/5234-5.html
Troubleshoot commands:
- show spantree vlan_id —Shows
the current state of the spanning tree for this VLAN ID, from the
perspective of the switch on which you issue the command.
- show spantree summary —Provides a summary of connected spanning tree ports by VLAN.
- show spantree statistics —Shows spanning tree statistical information.
- show spantree backbonefast —Displays whether the spanning tree BackboneFast Convergence feature is enabled.
- show spantree blockedports —Displays only the blocked ports.
- show spantree portstate —Determines the current spanning tree state of a Token Ring port within a spanning tree.
- show spantree portvlancost —Shows the path cost for the VLANs on a port.
- show spantree uplinkfast —Shows the UplinkFast settings.
No comments:
Post a Comment