QoS = against the classic FIFO. Melawan FIFO klasik.
FIFO menyebabkan semua trafik sama. Trafik yang berurgensi lebih penting di
QoS bisa dilihat di penerbangan.
Kelas Ekonomi
Kelas Bisnis
Atau gak usah jauh-jauh, analaogi QoS bisa dilihat di tukang pangkas.
Jumlah tukang pangkas
Jumlah rata-rata pasien per tukang pangkas per jam.
QoS mechanism:
1. Classification --> NBAR and DSCP
2. Marking --> CB-Marking
3. Congestion Management --> LLQ
4. Shaping --> CB-Shaping or FRTS
5. Link Efficiency --> Header Compression and LFI
QoS mechanism: How can we implement this below picture:
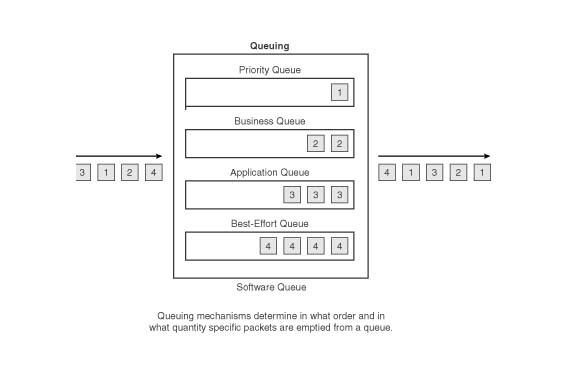
1st. define how many queue? 5
